| |
|
Agile Project Management is a
strategically aligned collection
of short iterations (Sprints).
|
|
|
| |
|
Benefits ▪
Principles ▪
Components ▪
Applicability
|
|
|
| |
With an agile
approach to management of complex and/or
creative
projects, it is best to take next-step
decisions at the last possible moment when you
benefit from the maximum information,
experience, and understanding.
This
approach enhances responsiveness to change,
improves delivery speed, and increases team
engagement by fostering transparency and
customer-centric development. |
|
 |
| |
Agile Project
Management
Agile PM uses short, fixed-length
iterations called Sprints, typically lasting 2–4 weeks. Each Sprint
is a small cycle of planning, execution, and review.
Sprints are further divided into
prioritized tasks, or User Stories, based on value and risk.
Progress is tracked through Daily
Standup Meetings – brief, 15‑minute check‑ins where team members
share what they completed yesterday, what they plan to do today, and
any obstacles.
At the end of each Sprint, the team
presents the completed work in a Sprint Review, giving the client a
chance to provide feedback or accept the results. |
|
Project Management
Strategic PM
Radical PM
Innovation PM
Project Leader
Skills
Team-based Skills
Entrepreneurial Skills
Self-Assessment
AImpowerment
Human-AI Synergy |
|
| |
|
Agile management is an
iterative,
flexible approach to project
management that breaks large and
complex projects into small,
manageable tasks completed in
short cycles (sprints).
|
|
|
| |
|
Agile management applies Agile
principles and
Lean Management to project
and team processes, emphasizing
iterative progress,
collaboration, and adaptability.
It breaks projects into
manageable stages, enabling
continuous feedback and
improvement.
Popular frameworks
include Scrum
(short, time-boxed sprints),
Kanban
(visualizing workflow to manage
capacity),
and Extreme Programming (XP).
|
|
|
| |
|
Core
Principles and
Frameworks
Core Principles:
Emphasizing individuals and
interactions over tools, working
software over documentation,
customer collaboration over
contract negotiation, and
responding to change over
following a plan.
Key Frameworks: Common
methodologies include Scrum,
Kanban, and Extreme Programming
(XP).
Extreme Programming (XP) is an
Agile methodology focused on
improving software quality and
responsiveness to changing
requirements. It emphasizes
simplicity, continuous
feedback, and short development
cycles. Key practices include
pair programming, test-driven
development, and frequent
releases. XP enhances
collaboration and adaptability,
making it ideal for dynamic
project environments. As a
subset of Agile, XP prioritizes
customer satisfaction and
technical excellence through
disciplined, iterative
processes. |
|
|
| |
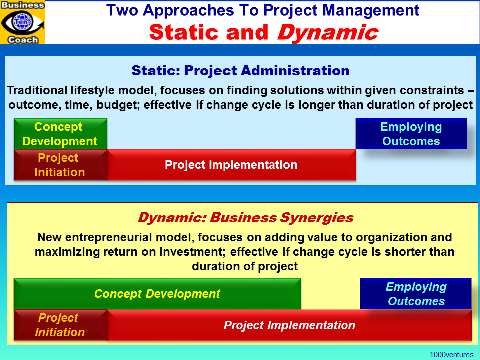
Iterative Process
Innovation projects involve continuous
cycles of planning, building, testing, and
reviewing, allowing for adjustments based on
real-time feedback. They don't lock down
design earlier than absolutely necessary not to
miss emerging opportunities. |
|
 |
| |
|
Key
Components and
Benefits
Flexibility: Teams can
easily shift direction and
reprioritize tasks based on
evolving requirements.
Collaboration: High
involvement between team members
and
stakeholders ensures the
final product aligns with user
needs.
Risk Mitigation: Regular,
small releases (increments)
allow for quicker detection of
issues, reducing the risk of
major project failure...
More
Improved Efficiency: By
focusing on value-driven
development, teams can reduce
rework and speed up delivery.
|
|
|
| |
|
Applicability
Agile management is now widely
used in software development,
marketing,
education, finance, and
other industries that require,
adaptation to changing
environments. It is most
effective for projects with
evolving requirements or where
quick, functional iterations are
valuable.
|
|
|
| |
|
How to use this information
|
|
|
|
|