| |
|
SWOT stands for Strengths,
Weaknesses, Opportunities,
Threats
|
|
|
 |
|
What is SWOT
Analysis?
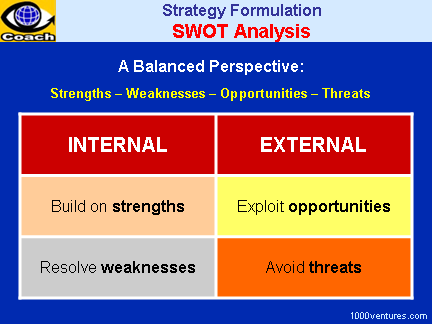
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities
and Threats (SWOT) analysis is a
strategy development tool that matches internal organizational
strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats. |
|
| |
|
Successful
Businesses build
on their strengths, correct
their weaknesses and protect
against internal vulnerabilities
and external threats. They also
keep an eye on their overall
business environment and spot
and exploit new opportunities
faster than competitors.
SWOT analysis is a tool that
helps many businesses in this
process.
|
|
|
| |
SWOT Analysis is the Key
Component of Strategic
Development. It can prompt
actions and responses.
SWOT analysis is based on the
assumption that if managers can
carefully review such strengths,
weaknesses, opportunities, and
threats, a useful strategy for
ensuring organizational success
will become evident to them.
|
|
|
| |
|
"So in war, the way is to avoid
what is strong and to strike at
what is weak. Water shapes its
course according to the nature
of the ground over which it
flows; the soldier works out his
victory in relation to
the foe whom he is facing."
~
Sun Tzu,
The Art of War
|
|
|
| |
Contributing Factors
Strengths:
sustainable competitive
advantage, ability,
people 10+, resources,
weakness of the competition, or
the opposing sources.
Weaknesses:
signs of losing organization,
failures, defeats, loses, and
inability to match up with the
dynamic situation of growth and
the change.
Opportunities:
possibilities of what can be
done and where effectiveness is
possible.
Threats: changes in
business environment, PEST
forces – political, economic,
social, technological.
|
|
Sustainable Competitive
Advantage (SCA)
Sources of
SCA
Distinctive Capabilities
Leading
vs. Lagging Companies
Characteristic of Most
Innovative Companies |
|
|
|
|
Strengths
Two factors contribute to your
strengths: ability and resources
available.
Ability is evaluated on 3
counts:
1. Versatility: your ability to
adapt to an ever changing
environment;
2. Growth: your ability to
maintain a continuing growth;
3. Markets: your ability to
penetrate or create new markets.
The strength of resources has
three dimensions:
1. Availability: your ability to
obtain the resources needed;
2. Quality: the quality and
up-to-dateness of the resources
employed;
3. Allocation: your ability to
distribute resources both
effectively and efficiently.
Weaknesses
Your weaknesses are determined
through failures, defeats,
losses and inability to match up
with the dynamic situation and
rapid change.
The weaknesses may be rooted in
lack of managerial skills,
insufficient quality,
technological backwardness,
inadequate systems or processes,
slow deliveries, or shortage of
resources.
|
|
|
|
|
Opportunities
Opportunities are abundant. You
must develop a formula which
will help you define what comes
within the ambit of an
opportunity to focus on those
areas and pursue those
opportunities where
effectiveness is possible. The
formula must define
product/service, target market,
capabilities required and
resources to be employed,
returns expected and the level
of risk allowed.
Weaknesses of your competitions
are also opportunities for you.
You can exploit them in two
following ways:
1. Marketing warfare: attacking
the weak leader's position and
focusing all your efforts at
that point, or making a
surprise move into an
uncontested area.
2. Collaboration: you can use
your complementary strengths to
establish a
strategic alliance with your
competitor.
Threats
External threats arise from
political, economic, social,
technological (PEST)
forces. Technological
developments may make your
offerings obsolete. Market
changes may result from the
changes in the customer needs,
competitors' moves, or
demographic shifts. The
political situation determines
government policy and taxation
structure.
|
|
|
|