| |
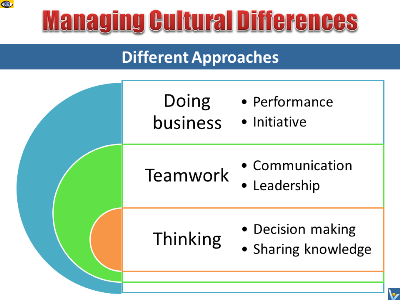
Cultural Differences
Ideological and
cultural differences top the
list. In evaluating joint
venture partners, most companies
don’t perform a proper
compatibility and integration
analysis. Neither make they a
thorough evaluation of
corporate culture and
management style. As a result,
they fail to find a way to blend
their differences, which makes
their joint ventures unstable..
|
|
|
|
|
|
Insufficient Planning
Insufficient planning is also
one of the most prevalent
reasons for failed joint
ventures. Too often, a joint
venture “plan” consists of
nothing more than a statement of
each party’s intended
contributions to the project and
their respective share of the
profits. This seldom works.
What the Plan Should Include
If the parties wish their joint
venture to succeed, they should
agree to a comprehensive written plan upfront. The philosophy governing
expectations and objectives of the joint venture should be clear.
The plan should include provisions
for future contributions, risk reduction,
logistical issues, governance of the joint venture, dispute resolution,
ownership of jointly-developed assets, including
intellectual property.
The term and termination of the joint venture, including provisions for winding
up its business should also be included in the plan.
|
|
| |
Other reasons of joint venture failure
include poor commitment; disagreement over operating policies,
strategies, and tactics; and differences in the approach towards
management style and
systems.
In particular, Hewitt lists these
factors that contribute to the poor track record of international
joint ventures:
▪ Conflict over delegation of
decision-making to the local joint venture management by a foreign
partner which sees the JV operations as only a small part of the
global picture and is trying to
maximize profits globally, while the local partner is trying to
maximize profits locally.
▪ Disagreement between the partners
over operating policies, strategies, and tactics in the local
market.
▪ Differences in the approach of each
partner towards management style (decision-making, communication,
delegation, and so on) and systems (performance
management, accounting, control, and so on)
|
|
Benefits
of Joint Ventures
Forming a
Successful Joint Venture (JV):
Factors To Be Considered
Model MoU
Business
Plan of a Joint Venture
Governing
Structure of a Joint Venture
HR
Strategies
HR Actions
4Ps of
Good Partnerships
Win-Win
Mindset
4 Levels
of Problem Solving |
|
| |
|
How to use this information
|
|
|
| |
①
"Adapt what is useful, reject
what is useless, and add what is
specifically your own."
~
Bruce Lee
②
Sleep on this information – your
powerful
superconscious mind will
tell you how to use it when you
wake up
|
|
 |
|
|