|
|
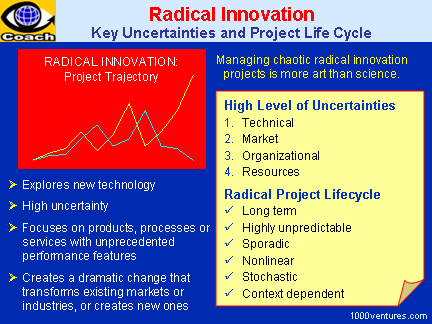
Fuzzy logic is a system of logic that allows
for degrees of uncertainty, rather than depending on absolute truth-values,
and that is used to make human thought processes or imprecise information
accessible to computers.
While the situations that fuzzy logic addresses
are ambiguous, fuzzy logic itself is a very defined methodology. Modern
→
business and technology leaders use the managerial equivalent of fuzzy logic
to address the ambiguity of the fuzzy front end.
The core elements of this approach include:1
-
"No plan survives contact with the
enemy."
→
Map is not the territory. Whatever plan you create will not be one you
will ultimately implement.
-
Having a plan is better than not having one.
Having a collective understanding of
→
business context,
intentions
and
→
guiding principles
will enable your
team to select and communicate alternate directions
knowledgeably and quickly.
-
Make decisions at an early phase.
You'll never have all the data. Waiting for more data can go
indefinitely. Besides, much of what is called data, such as
market
research, is more opinion than fact.
>>>
-
→
Be flexible. Ongoing thinking and action brings strategy to life.
Having built a consensus around the market, competition, and technology
and having picked a direction, never turn your radar off. Scan
constantly for new developments,
reassess your past decision, and be ready to
retarget briskly when
needed. Locking into any plan when the competitive context continues to
change is a foolish approach.
>>>
-
Think of
product and service families.
"One-off thinking yields one-off products. One-off projects, even when
successful, are very expensive. One-off projects live by themselves,
with little connection to past or future efforts, and require more
energy, specialized skills, and tools from every corner of the firm."1
-
Find a partner. Don't do it alone. Focus internally on
where you
can make a world class contribution and then leverage the development
risk, investment and reward with others who can bring their
complementary skills, resources and capabilities to the party. With
partnerships, your
→
capabilities,
capacity, and accountability only begin inside your office walls.
-
Balance
customer feedback with your own understanding of the
technology potential. "Listen
to your current customers, but don't always believe them. Often the
→
benefits of new technology move
faster than your current
customers are
willing to accept."1 Remember however that although customers
can be overly conservative, technology push by itself rarely wins.
-
Focus on opportunity, not financial returns.
→
Money isn't everything. Measuring return, risk, and investment solely in
terms of dollars is a mistake.
Capabilities grow through use, and how
fast they grow is critical to
→
your success. Jump into the market
before the financial returns meet your requirements.
 Kore 10 Innovative
Thinking Tools
Kore 10 Innovative
Thinking Tools
Kore 10 Tools help
innovators approach
creation of
entrepreneurial
strategies and
anticipation of opponents' moves more
systematically.
The Kore 10 Tools help also
innovation leaders and
radical project managers strengthen and
synergize the
most important
areas of innovation...
More
|