 |
Hard skills make you eligible.
Soft skills make you desirable.
~
Vadim
Kotelnikov |
|
Definition of Soft Skills
Soft skills are a cluster of
productive capabilities that
characterize one's relationships
in a social environment.
It is an umbrella term for
skills under three key
functional elements:
achievement know-how,
people skills, and social
skills.
|
|
| |
|
The Vital Importance of Soft
Skills
|
|
|
| |
As business is
people, soft skills are more important than hard
skills because they are the foundation of
thinking, cooperation, management, innovation,
marketing, etc.
The influence of soft skills on the outcome of
business activities depends on the circumstances
in which the business activity takes place. |
|
 |
 |
|
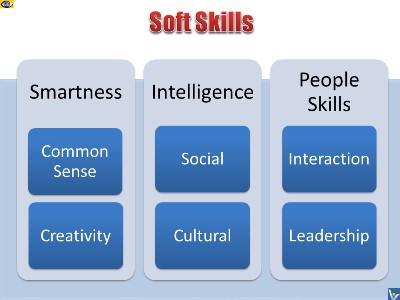
Soft skills are a synergistic
combination of common sense,
creative
thinking skills,
decision making
skills, problem solving skills, empowering attitudes, the
ability to make a desired
first impression and to be
charismatic, people skills, social skills, communication
skills, the ability to build
rapport, the ability to
lead,
teamwork, social intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, emotional intelligence,
cultural intelligence, and empathy among others. |
|
| |
|
Development of Soft Skills
The development of soft skills
is more difficult than the
development of hard skills.
|
|
|
| |
While hard skills
can be learned studying from a book or from
trainings, development of soft skills needs a
combination of environment and other people to
be mastered. It requires addressing
multi-dimensional challenges, actively
interacting with others on an ongoing basis and
being willing to learn from all sorts of
feedback both verbal and situational. |
|
 |
| |
Interpersonal
Intelligence (IPQ).
Interpersonal Intelligence (IPQ) is the ability
to understand others and interact effectively
with them...
More |
|
Win-Win Mindset
12 Zodiac Rules |
|
| |
|
How to use this information
|
|
|
| |
|
①
"Adapt what is useful, reject
what is useless, and add what is
specifically your own."
~
Bruce Lee
②
Sleep on this information – your
powerful
superconscious mind will
tell you how to use it when you
wake up
|
|
 |
Interpersonal Intelligence
Creativity
In the digital economy where
the large majority of the work can be done by computers,
artificial intelligence systems and smart machines, the
primary role of human beings is to use their imagination and
creativity to invent new things and to solve problems in
outside-the-box ways.
Leadership
Soft skills form the basis of
successful leadership and are, therefore, highly important
for those in leading positions. Leaders are to inspire, to
provide a strategic direction, to align, motivate and
energize people in order to achieve desired goals.
Leadership is a process of influence through a series of
interactions between a leader and their followers. In order
to be effective in these roles, the leader has to possess
relevant soft skills.
Communication
Effective communication inside
the company is the foundation of successful business
activities. Communication allows employees at all levels to
coordinate their actions to achieve a common objective.
Decision
Making
Although strategic plans are
developed by a top management team, due to the scope and
complexity of business operations, top managers have to rely
on their staff to assist them in the decision-making
process. Staff members can broaden the understanding of
current business activities by developing situational
awareness and assisting top managers in building their
situational understanding by providing relevant information
and recommendations regarding business activities.
Cross-Cultural Competency
A globally connected world is
a key driver of structural change for the global workforce.
The diversity of stakeholders
is an important point to consider. Employee, customers,
partners, competitors are all made up of people of different
ethnical backgrounds, who have different views, perceptions,
beliefs, and values.
Innovation became a systemic
phenomenon. It is achieved through synergizing diversities
and is increasingly more dependent on the collaboration
between actors from different cultural backgrounds who
combine their own perceptions, thinking habits and expertise
to create something new. This happens on all levels −
individual, team, institutional. Diversity of thought
increases creativity and, with it, the innovation potential
of individuals, teams, corporations and joint ventures.
Business activities that take
place abroad emphasize the importance of cultural
intelligence and effective cross-cultural communication
between the business and local people. Unless company
representatives have good understanding of the local
traditions and values, they might behave in such a way that
is considered offensive or inappropriate in another culture
and facilitate conflict, putting the whole local business at
risk. In order to effectively perform business activities in
a different cultural setting, company representatives must
possess such soft skills, as sociocultural competence and
empathy.
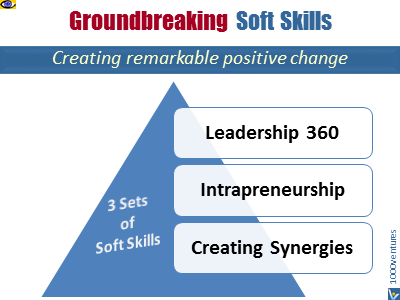
Groundbreaking Soft Skills
empower you to create remarkable positive change in
yourself, your organization and its business.
|
Building Leadership Skills
For Your Business |
Skills 4.0: Focus
on Soft Skills
In today’s rapidly
changing dynamic markets, companies need an
adaptable and flexible workforce in order to be
ready to address potential skills gaps and
talent shortages. It is mostly soft skills that
are required to rise to the challenges brought
on by the megatrends and rapid change in
technology, business models, organizational
designs, and customer needs.
The Fourth
Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0) makes
formal degrees (hard skills) comparatively less
important, with personal skills (soft skills)
becoming more critical. People need new Skills
4.0 not only to cope with rapid, relentless,
unpredictable, an often transformational change,
but to thrive in it and to create change
themselves.
The new job
marketplace calls to focus on
capabilities instead of qualifications.
Instead of looking for hard-skill professionals,
companies look now more often for employees who
are open to change.
→
Creative Dissatisfaction,
→
Creativity,
critical thinking and
→
Problem Solving
emerged as the top skills required by industry.
At the top management level, the three top
soft skills for businesses are
complex problem-solving, coordinating with
others, and managing people.
Employees need to
be trained for skills, especially
soft skills,
not tasks. Machines take care of
quality control, while employees need to
shift their focus on the things machines so far
cannot do, such as
→
Innovation,
→
Your
Interpersonal Skills,
and
emotional intelligence. Employees have to be
open to change, possess greater flexibility to
adapt to new roles, and build
cross-functional expertise through
continuous interdisciplinary
→
learning. |

|
|