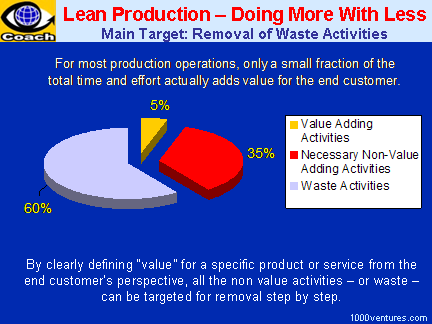
 |
|
Lean is about doing more with
less: less time, inventory, space, labor, and money.
Lean manufacturing is about commitment to eliminating waste, simplifying procedures and
speeding up production.
The idea is to pull inventory through based on
customer demand. |
|
| |
Lean Manufacturing also
known as the Toyota Production
System (TPS)
is, in its most basic form,
the systematic elimination of
waste overproduction,
waiting, transportation,
inventory, motion,
over-processing, defective units
and the implementation of the
concepts of continuous flow and
customer pull. By continually
focusing on waste reduction,
lean enterprises can achieve
unlimited benefits.
Five areas drive lean
manufacturing: cost, quality,
delivery, safety, and morale.
Value is defined by the
ultimate
customers needs.
|
|
Continuous
Improvement Firm (CIF)
Kaizen and Lean Manufacturing
Kaikaku-Kaizen Journey
Implementation
Suggestion
System
Examples
of CIF |
|
|
|
|
Key Features of Lean
Production
compared
to Traditional Mass Production |
-
Reduced Setup Cost and
Times (for semi-versatile
machinery such as big stamping presses)
from months to hours thus making
small-lot production economically viable; achieved by organizing
procedures, using carts, and training workers to do their own setups,..
More
|
|
Strategy of Lean Production |
|
|
|
Benefits of Lean Production
Establishment and mastering of a
lean production system would allow you to achieve the following benefits:
-
Waste
reduction by 80%
-
Production cost reduction by 50%
-
Higher
→
quality
-
Manufacturing cycle times decreased by 50%
-
Labor reduction by 50% while maintaining or
increasing throughput
-
Inventory reduction by 80% while increasing
customer service levels
-
Capacity in current facilities increase by
50%
-
Higher
→
profits
-
Higher system flexibility in reacting to
changes in requirements improved
-
More strategic focus
-
Improved cash flow through increasing
shipping and billing frequencies
However, by continually focusing
on waste reduction, there are truly no end to the benefits that can be
achieved.
→
Kaizen: 5 Principles
→
Kaizen Culture:
8 Key Elements
→
Implementing Kaizen:
7 Conditions
Characteristics
of Lean Manufacturing Systems
-
Close integration of the whole
→
value chain from raw material to finished product through partnership
oriented relations with suppliers and distributors.
-
→
Team based work
organizations with multi skilled operators empowered to make decisions
and improve operations with few indirect staff...
More
 Toyota Toyota
 Three Small- and Medium-Sized Firms, U.S.A. Three Small- and Medium-Sized Firms, U.S.A.
Smaller and
mid-sized organizations pride themselves on being nimble quick to respond
and to
seize
opportunities. Many believe smaller size is more manageable; and that
internal communications in a
smaller group
can be maintained so employees can take ownership of more than their own
corner of the enterprise. One key to success is maximizing resources and
discovering inventive ways to overcome budget limitations. Another trend is
moving from a PUSH system
building to
forecasts
to a PULL system, building in response to
orders...
More
|

|
References:
-
Relentless Growth, Christopher Meyer
-
"Competitive Manufacturing Management", John M. Nicholas
-
"The Lean Journey" White Paper by Oracle Corporation
-
"TPS vs. Lean and the Law of Unintended
Consequences," Art Smalley
-
"Lean Thinking," James Womack and Daniel Jones
-
Lean Manufacturing That Works, Bill Carreira
-
The
Toyota Way, Jeffrey Liker
-
Toyota
Production System,, Taiichi Ohno
-
"Kanban
Just-In-Time at Toyota," Japan Management Association
-
"Lean
Production Simplified," Pascal Dennis, John Shook
-
"The
Lean Manufacturing Pocket Handbook," Kenneth W. Dailey
-
"Lean
Six Sigma," Michael
L. George
-
Kaikaku: The Power and Magic of Lean, Norman Bodek
|
|
|
|